What is Transform+
Transform + allows you to apply mathematical functions to the size, position, color etc of a shape.
Why is this needed?
Illustrator has a Transform Each tool, however while you can scale and move shapes you are limited in setting their size and other settings. With basic settings Transfrom+ allows you to do everything the Transform Each tool does, however when you start using mathematical functions you have a very powerful tool to manipulating your artwork.
How does it work
For every shape selected the script gets a list of properties for the shape, You can then use these as variables to alter the shapes size, position, stroke and fill. The key feature is that you can use any variable in any field to calculate values - this can create some very powerful transformations.
Interface
Variables
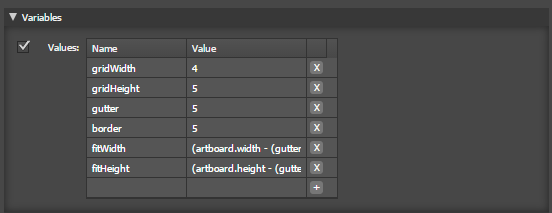
Here you can define variables to be used in other sections, Use to pre-calculate or as a basic options menu allowing the user to easily change settings.
- Name The Name of the variable
- Value The Value, Note that you can refer to previously defined variables in the value
Filter
Sort

All user selected items are in an array. Use this to pre-sort the items by criteria, such as color, width, area.
- Examples
- To sort by width [ width ]
- To sort by random number [ random(1) ]
- To sort by area [ area ]
- To sort by stroke width, but treat unstroked shape as if they had a width of 100 use [ stroked ? strokeWidth : 100 ] which is if stroked then strokeWidth else 100
Copies

Make copies of the selection rather than loop through the selection. The selected items will be treated as a group.
- Copies The number of copies to make, this can also be a variable or something like [ selection.width / 10 ]
- Copy from Source If ticked it will always copy the source selection, if unticked it will copy the last copy, For example, if you scaled the height by 90%, with this ticked all copies will be 90% of the original but the same size, unticked each copy will diminish in size.
- Examples
- To make 10 copies set to [ 10 ]
- To make a copy every 10mm of an artboard use copies: [ floor(artboard.width / 10) ] and then later set the x position based on the copy count x:[ count * 10 ]
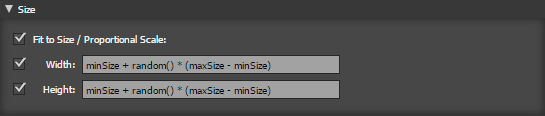
Size
- Fit to Size/Proportional Scale:
- If ticked and both width and height are set the scale is scaled proportionally to fit within the height and width
- If ticked and only the width or height are set the shape is scaled proportionally
- if unticked the only the width or height are changed independently.
- Width Sets the width of the shape,
- Height Sets the height of the shape,
- Examples:
- To scale just multiply by a number [width * 0.5 ] will scale by 50%
- To ensure the height does not exceed a maximum number of 100 use [ min(100, width) ]
- To round the width to be multiples of 10 use [ round(width / 10) * 10 ] or modulus math [ width - (width %10) ]
Transform
- 9 point position Set the rotation point based on the shape
- Rotate Rotates the shape by n degrees
- Examples:
- To rotate to a random angle use [ random() * 360 ]
- To rotate all shapes so they are landscape [ height > width ? 90 : 0 ] … if height is greater than the width, rotate by 90 degrees else rotate by zero degrees
- To rotate each shape 2 degrees more than the last [ index * 2 ]
- Rotate based on how much black ink in the fill or do not rotate if no fill [ filled ? fill.black * 3.6 : 0 ]
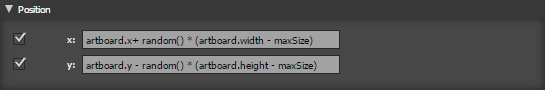
Position
- x Sets the x position of the shape
- y Sets the x position of the shape
- Examples
- Set each shape to be 10mm further away from the left of the artboard [ artboard.x + (index * 10) ]
- Align to the center of the artboard [ artboard.x + (artboard.width / 2) - (width / 2) ]
- butt fit each shape next to the first shape in a row so they line up - set x:[ index == 0 ? first.x : previous.x + previous.width ] and set y:[ first.y ]
- Set x to a random position on the artboard but make sure it does not go over the edge x:[ artboard.x + (artboard.width - width) * random() ]
- Complicated example to layout shapes in a grid 5 items acoss with 100mm wide and 150mm high
- x: [ artboard.x + (index % 5) * 100 ] … (index % 5) returns a number 0 to 4
- y: [ artboard.y + floor(index / 5) * 150) … floor(index / 5) returns the row number
Stroke

See table below for special color variables aviavable in this section
- Width Sets the width of the stroke IN POINTS
- Color Sets the Color - Choose either RGB or CMYK colors to set.
- Apply to un-stroked shape - Apply changes and settings to shapes with no stroke, otherwise shapes with no stroke are not affected
- Examples
- See the screenshot above for an example of how to set the stroke to be the same as the fill color
- Ensure all strokes are at least 0.25 points in width - set width:[ min( 0.25, strokeWidth ) ]
- Set the stroke to be 5% of the width of the shape with a maximum of 10 points and minimum of 1 point [ max( 1, min( 10, width * 0.05 ) ) ]
Fill
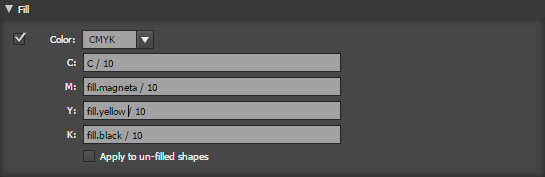
Set or modify the fill color See table below for special color variables aviavable in this section
- Color Sets the Color - Choose either RGB or CMYK colors to set.
- C/M/K/Y or R/G/B Set the color component, If this is blank that colour channel will remain unchanged, so for example if you set K to zero it will remove all black from the color
- Apply to un-fill shape - Apply changes and settings to shapes with no fill, otherwise shapes with no fill are not affected
- Example
- Tint a colour to 50% C:[ fill.cyan * 0.5 ]
- Invert an RGB color R: [ 255 - R ] - Using 'R' as shortcut for fill.red
- To eliminate any colour under 1% C:[ max(1, C) ] - Using 'C' as shortcut for fill.cyan
- To gamma adjust an RGB color R:[ 255 * (R / 255) ^ gamma ] or R:[ 255 * (R / 255) ^ (1/gamma) ]
Extendscript
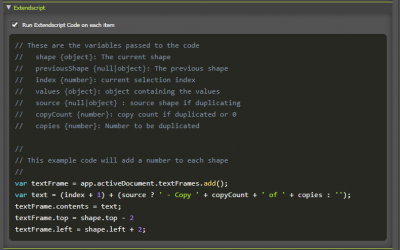 This will run Javascript code on each shape being transformed, giving you extra control on modifying the shape.
This will run Javascript code on each shape being transformed, giving you extra control on modifying the shape.
These are the variables passed to the code
- shape {object}: The current shape
- previousShape {null|object}: The previous shape
- index {number}: current selection index
- values {object}: object containing the values
- source {null|object} : source shape if duplicating
- copyCount {number}: copy count if duplicated or 0
- copies {number}: Number to be duplicated
Delete
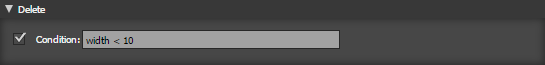
Set a condition which will delete the shape if it returns true
- Example
- Delete all shapes smaller than 10 x 10 - set condition: [ width < 10 and height < 10 ]
- Delete all shapes with no fill and no stroke - set contition: [ filled == 0 and stroked == 0 ]
Options
- Scale Positions Scale the position when resizing
- Scale Fill / Patterns Scale Fills and Patterns when resizing
- Scale Stroke Patterns Scale Strokes and Stroke Patterns when resizing
- Scale Gradients Scale Gradients when resizing
- Scale Strokes Scale Strokes ents when resizing
- Clear Selection Clear the selection when completed, same as Select None
- Apply to all items inside groups When ticked grouped items are treated as ungrouped shapes
- Size Units The units used for positioning (x / y) and size (height / width).
Complex Examples
See the pre-saved defaults that come with the install.
Variables and Functions (Technical bit)
Below are the variable, operators and functions you can use.
Shape Variables
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| area | number | area of the shape as calculated by illustrator, Maybe a negative number depending on path direction. |
| closed | 1 = true 0 = false | true of the shape is closed, false if it is open |
| stroked | 1 = true 0 = false | true if the shape has a stroke |
| strokeWidth | number | the Width of the stroke in points |
| stroke | color (see below) | the stroke color |
| filled | 1 = true 0 = false | true if the shape is filled |
| fill | color (see below) | the fill color |
| opacity | number | the opacity 0 - 100 |
| x | number | the shapes x coordinate in points |
| y | number | the shapes y coordinate in points |
| height | number | the shapes height in points |
| width | number | the shapes width in points |
| typename | string | A shapes typename such as PathItem, CompoundPathItem, GroupItem, MeshItem, RasterItem, SymbolItem, PlacedItem, TextFrame, TextPath Refer to the Javascript scripting reference for a full list of typenames |
References to other objects / shapes
These objects give you access to the variables of other shapes
| Variable | Type/Properties | Description |
|---|---|---|
| start. | shape For Example start.width start.opactiy start.x …. | Refers to the starting variables of the shape, for example if you set the value of a shape it changes, you can refer to start.width to get the value of the width before any changes were made |
| first. | shape For Example first.height first.x first.stroked …. | Refers to the FIRST shape in the selection, this is also the LAST shape selected by the user, you can use this to align all shapes to the first shape. \\For example you can set the x position of all elements to be the same as the first x: first.x |
| previous. | shape For Example previous.area previous.closed previous.fill …. | Refers to the previous shape, for example to but fit the current shape to the previous shape you can set the x position x: previous.x + previous.width |
| artboard | artboard.x artboard.y artboard.height artboard.width | The artboard size, properties are x, y, height, width for example to set the width of a shape to half the artboard width use width: artboard.width/ 2 |
| selection | selection.x selection.y selection.height selection.width selection.count} | The selection size, properties are x, y, height, width plus also count which is the number of shapes in the selection |
Other Variables
In addition to the shape variables you can also use
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| index | number | The index of the shape, if 5 shapes are selected then this will range form 0 to 4 |
| count | number | When using the copies features, count is the copy number, First copy count is 0 |
Color Variables
Color values can be referenced using dot notation for example fill.cyan
| Variable | Shorthand* | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| mode | string | either 'RGB' or 'CMYK' | |
| cyan | C | number | 0 - 100 |
| magenta | M | number | 0 - 100 |
| yellow | Y | number | 0 - 100 |
| black | K | number | 0 - 100 |
| red | R | number | 0 - 255 |
| green | G | number | 0 - 255 |
| blue | B | number | 0 - 255 |
* Color Shorthand
These only work in the fill and stroke color settings, these directly relate to the fill or stroke colour , you can just use the capital letter of the color you want to use , they are C, M, Y, K, R, G, B
For example if you wanted to divide the cyan value by two instead of writing
fill.cyan / 2
you can just write
C / 2
Functions
Size finctions
| Operator | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mm(n) | points | Convert n milimeters to points |
| cm(n) | points | Convert n centimeters to points |
| m(n) | points | Convert n meters to points |
| inch(n) | points | Convert n inches to points |
| foot(n) | points | Convert n feet to points |
Unary operators (math)
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| -x | Negation |
| +x | Unary plus. This converts it's operand to a number, but has no other effect. |
| x! | Factorial (x * (x-1) * (x-2) * … * 2 * 1). gamma(x + 1) for non-integers. |
| abs x | Absolute value (magnatude) of x |
| acos x | Arc cosine of x (in radians) |
| acosh x | Hyperbolic arc cosine of x (in radians) |
| asin x | Arc sine of x (in radians) |
| asinh x | Hyperbolic arc sine of x (in radians) |
| atan x | Arc tangent of x (in radians) |
| atanh x | Hyperbolic arc tangent of x (in radians) |
| ceil x | Ceiling of x — the smallest integer that’s >= x |
| cos x | Cosine of x (x is in radians) |
| cosh x | Hyperbolic cosine of x (x is in radians) |
| exp x | e^x (exponential/antilogarithm function with base e) |
| floor x | Floor of x — the largest integer that’s <= x |
| length x | String length of x |
| ln x | Natural logarithm of x |
| log x | Natural logarithm of x (synonym for ln, not base-10) |
| log10 x | Base-10 logarithm of x |
| not x | Logical NOT operator |
| round x | X, rounded to the nearest integer, using “gradeschool rounding” |
| sin x | Sine of x (x is in radians) |
| sinh x | Hyperbolic sine of x (x is in radians) |
| sqrt x | Square root of x. Result is NaN (Not a Number) if x is negative. |
| tan x | Tangent of x (x is in radians) |
| tanh x | Hyperbolic tangent of x (x is in radians) |
| trunc x | Integral part of a X, looks like floor(x) unless for negative number |
Predefined Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| random(n) | Get a random number in the range [0, n). If n is zero, or not provided, it defaults to 1. |
| fac(n) | n! (factorial of n: “n * (n-1) * (n-2) * … * 2 * 1”) Deprecated. Use the ! operator instead. |
| min(a,b,…) | Get the smallest (minimum) number in the list |
| max(a,b,…) | Get the largest (maximum) number in the list |
| hypot(a,b) | Hypotenuse, i.e. the square root of the sum of squares of its arguments. |
| pyt(a, b) | Alias for hypot |
| pow(x, y) | Equivalent to x^y. For consistency with JavaScript's Math object. |
| atan2(y, x) | Arc tangent of x/y. i.e. the angle between (0, 0) and (x, y) in radians. |
| if(c, a, b) | Function form of c ? a : b |
Operator Precedence
| Operator | Associativity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (…) | None | Grouping |
| f(), x.y | Left | Function call, property access |
| ! | Left | Factorial |
| ^ | Right | Exponentiation |
| +, -, not, sqrt, etc. | Right | Unary prefix operators (see below for the full list) |
| *, /, % | Left | Multiplication, division, remainder |
| +, -, || | Left | Addition, subtraction, concatenation |
| ==, !=, >=, ⇐, >, < | Left | Equals, not equals, etc. |
| and | Left | Logical AND |
| or | Left | Logical OR |
| x ? y : z | Right | Ternary conditional (if x then y else z) |
Release Notes
- 1.4.0 - October 2023
- Added Extendscript code
- 1.3.1 - 17 December 2017
- Requires PowerScripts 3.4.2
- CC2018 Fixes
- Saving presets also saves accordions status of expanded to closed.
- 1.3.0 - 25 November 2017
- Added typename property
- Added Filter section
- Added Delete section